a change in the direction of high velocity fluid jet that issues from a nozzle.
Water turbine is a prime mover, which uses water as the working substance to generate power.
A water turbine uses the potential and kinetic energy of water and converts it into usable mechanical
energy. The fluid energy is available in the natural or artificial high level water reservoirs,
which are created by constructing dams at appropriate places in the flow path of rivers. When water
from the reservoir is taken to the turbine, transfer of energy takes place in the blade passages of the unit.
Hydraulic turbines in the form of water wheels have been used since ages; presently their application
lies in the field of electric power generation. The mechanical energy made available at the turbine shaft
is used to run an electric generator, which is directly coupled, to the turbine shaft. The power generated
by utilizing the potential and kinetic energy of water has the advantages of high efficiency, operational
flexibility, low wear tear, and ease of maintenance.
Despite the heavy capital cost involved in constructing dams and reservoirs, in running pipelines
and in turbine installation (when compared to an equivalent thermal power plant) different countries
have tried to tap all their waterpower resources. Appropriate types of water turbines have been installed
for most efficient utilization. A number of hydro-electric power plants have and are being installed in
India too to harness the available waterpower in the present crisis of fast idling energy resources. Hydroelectric
power is a significant contributor to the world’s energy sources.
Types Of HydrualicTurbines
Hydraulic turbines are required to transform fluid energy into usable mechanical energy as efficiently
as possible. Further depending on the site, the available fluid energy may vary in its quantum of potential and kinetic energy. Accordingly a suitable type of turbine needs to be selected to perform the required job.Based upon the basic operating principle, water turbines are categorized into two types depending on whether the pressure head available is fully or partially converted into kinetic energy in the nozzle.
Water (hydraulic) turbines have been broadly classified as,
1. Impulse 2. Reaction
1. Impulse Turbine wherein the available hydraulic energy is first converted into kinetic energy by
means of an efficient nozzle. The high velocity jet issuing from the nozzle then strikes a series of
suitably shaped buckets fixed around the rim of a wheel (Fig. 1.16). The buckets change the direction of
jet without changing its pressure. The resulting change in momentum sets buckets and wheel into rotary
motion and thus mechanical energy is made available at the turbine shaft. The fluid jet leaves the runner
with a reduced energy. An impulse turbine operates under atmospheric pressure, there is no change of
static pressure across the turbine runner and the unit is often referred to as a free jet turbine. Important
impulse turbines are: Pelton wheel, Turgo-impulse wheel, Girad turbine, Banki turbine and Jonval turbine
etc., Pelton wheel is predominantly used at present.
2. Reaction Turbine wherein a part of the total available hydraulic energy is transformed into
kinetic energy before the water is taken to the turbine runner. A substantial part remains in the form of
pressure energy. Subsequently both the velocity and pressure change simultaneously as water glides
along the turbine runner. The flow from inlet to outlet of the turbine is under pressure and, therefore,
blades of a reaction turbine are closed passages sealed from atmospheric conditions.
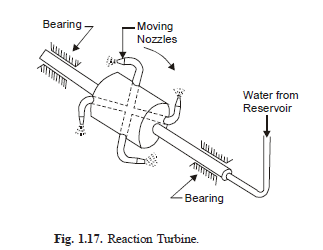
Fig. 1.17 illustrates the working principle of a reaction turbine in which water from the reservoir
is taken to the hollow disc through a hollow shaft. The disc has four radial openings, through tubes,
which are shaped as nozzles. When the water escapes through these tubes its pressure energy decreases
and there is increase in kinetic energy relative to the rotating disc. The resulting reaction force sets the
disc in rotation. The disc and shaft rotate in a direction opposite to the direction of water jet. Important
reaction turbines are, Fourneyron, Thomson, Francis, Kaplan and Propellor turbines Francis and Kaplan
turbines are widely used at present.
Comparison Between Impulse And Reaction Turbine
The following table lists salient points of difference between the impulse and reaction turbines
with regard to their operation and application.


Awsome website! I am loving it!! Will be back later to read some more.
I am bookmarking your feeds also
I think this is one of the most vital info for
me. And i’m glad reading your article. Buut waht to remark on some general things, Thhe sitte style is great,
thhe articles is really excellent : D. Good job, cheers